Lesson 2 : Formal and Informal Sector
The differences between the formal and informal sectors
Businesses operating in South Africa are divided into the formal and informal sector.
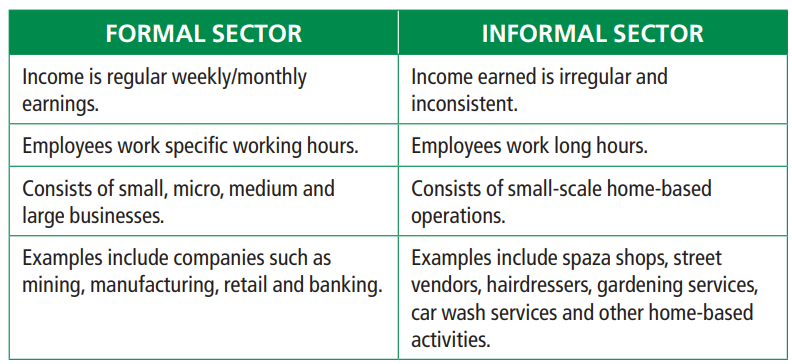
The formal sector is mainly characterized by small, micro, medium and large businesses with specific working hours and monthly salaries or weekly wages. These businesses have a specific aim of making a profit. Examples of businesses in the formal sector include mines, farms, manufacturers, construction, retailers, and insurance companies. The informal sector consists of small businesses with long working hours and irregular income. These small businesses are mostly started by the unemployed people who need to earn an income to buy necessities or pay for things such as water and electricity. Examples of businesses in the informal sector include food and flea markets, street vendors, and spaza shops.
With increasing unemployment in South Africa, the informal sector is growing bigger since many people are using their entrepreneurial skills to generate some form of income to survive.
Meaning and differences of the formal and informal sectors and examples of each
Formal sector
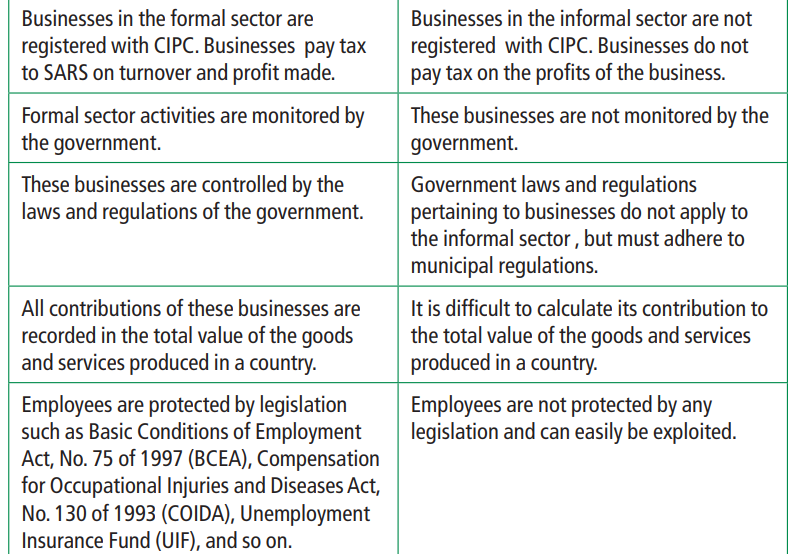
Businesses in the formal sector are registered and pay taxes. These businesses are required to register with the Companies and Intellectual Property Commission
(CIPC). Businesses have to register with the South African Revenue Services (SARS) and be liable to pay tax on turnover and profits at prescribed threshold.
Informal sector
Businesses in the informal sector are not registered with CIPC and do not pay tax on profits to SARS. The informal sector refers to those workers who are self-employed. Owners of
businesses in the informal sector take responsibility for the success and failure of their businesses.
Differences between formal and informal sectors

More differences
The importance of the formal and informal sector
Formal sector
• Business activities are included in the GDP figures of the country.
• Companies pay taxes on their profits.
• People who are employed at companies pay personal income tax.
• Provides employment to highly skilled, semi-skilled and unskilled labour.
• People working in the formal sector gain the necessary skills to start their
own businesses.
• Provides a large variety of goods and services to satisfy consumers.
Informal sector
• Encourages entrepreneurship and self-employment.
• Provides employment opportunities for communities and contributes to
poverty alleviation.
• People working in the informal sector gain work experience, which enables
them to apply for jobs in the formal sector.
• People start informal businesses to supplement their income earned in the
formal sector.
• It is easy to enter this sector and serves the needs of individuals.