Lesson 1 : Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sector
KEY CONCEPTS
- Primary sector: deals with the extraction of raw materials and natural
resources. - Secondary sector: involves the process of transforming raw materials into finished or unfinished products.
- Tertiary sector: refers to industries that offer services to other businesses and consumers.
- Formal sector: businesses in the formal sector are registered businesses
who pay taxes to the government. - Informal sector: businesses in the informal sector refer to businesses that are not registered and do not pay tax on the profits of the business.
- Private sector: consists of businesses owned, managed and controlled by individuals and organisations seeking to generate profit.
- Public sector: is the part of the economy, where goods and services are
provided by the government or local authorities carrying out the
task instead.
Introduction
Business sectors consist of businesses that are grouped together and classified into primary, secondary or tertiary sectors. How the business is classified depends on the nature of its product or service. The purpose of the classification is to determine the contribution of each sector and industry to the South African economy. Businesses play a huge role in making a meaningful contribution within the different sectors.

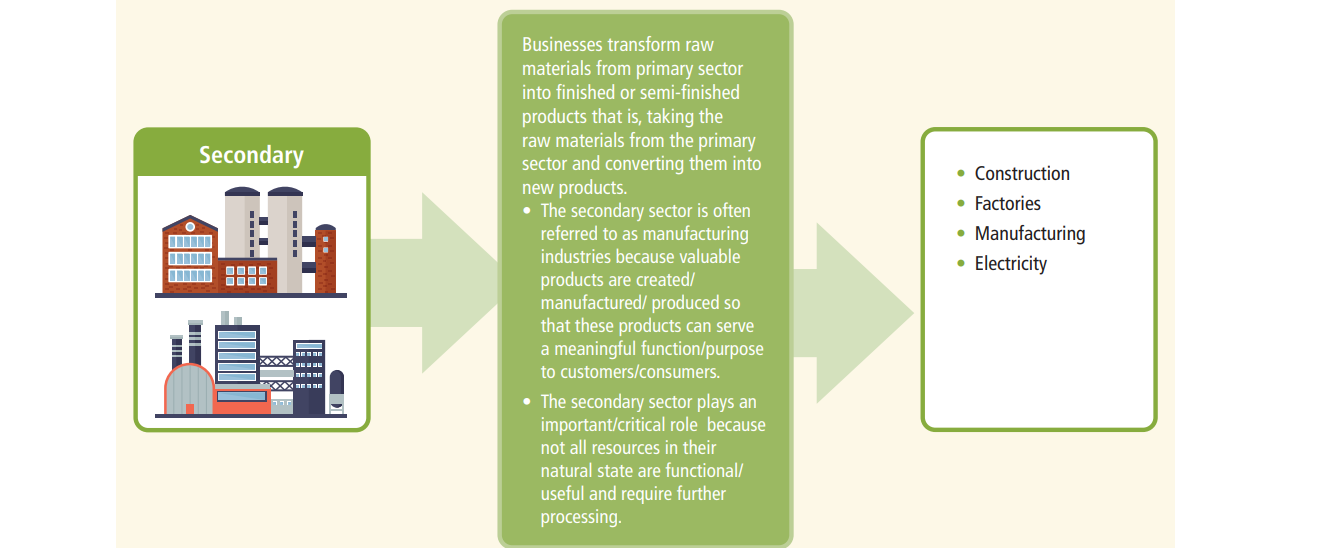

The relationship between the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors.
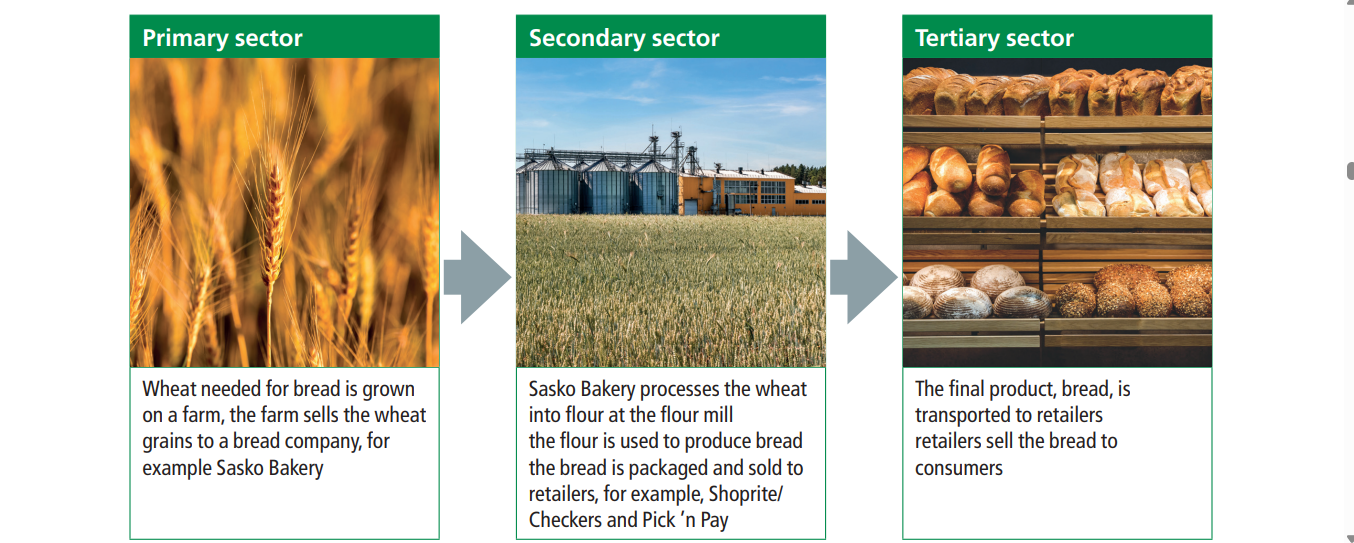
The sectors work together to create an economic chain of production. The primary sector gathers the raw materials, the secondary sector transforms the raw materials into useful goods. The tertiary sector sells the goods or services and supports the activities of the primary and secondary sectors.
Let us have a look at how a product such as BREAD reaches the table of a consumer.
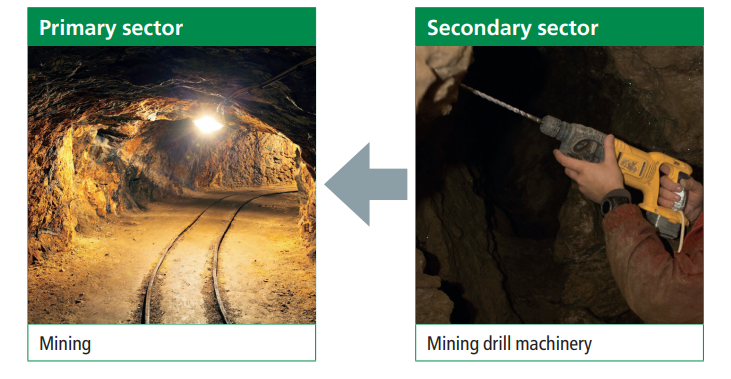
However, the relationship between the three sectors is not a linear one. The primary sector also depends on the secondary sector for manufactured goods such as machinery and equipment.
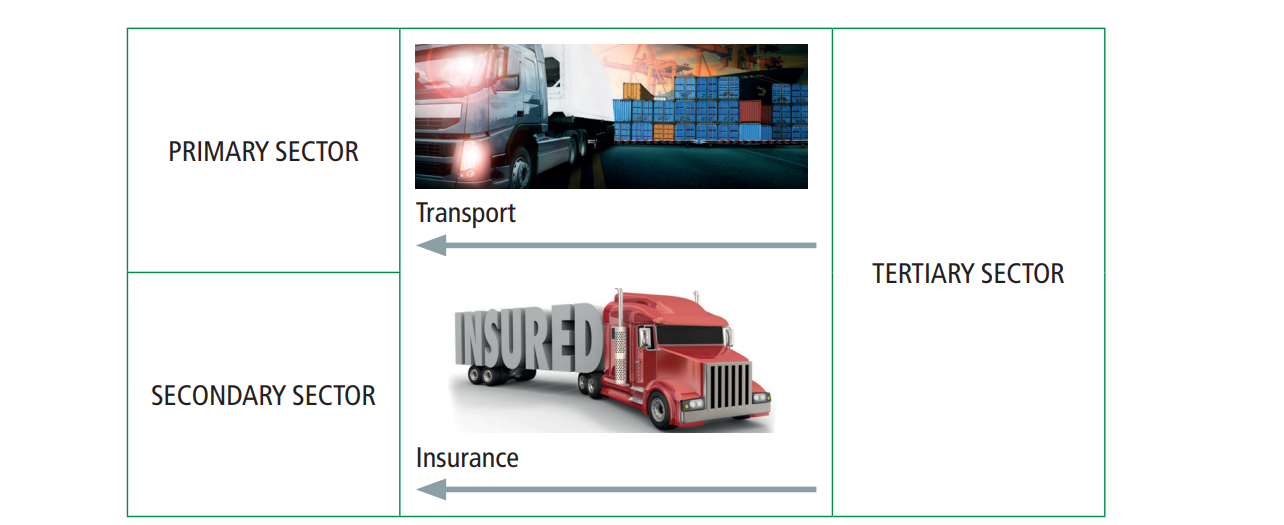
The primary and secondary sector also depends on the tertiary sector to provide services such as insurance and transport.